Search Engine Optimization Tutorial (An Introduction to SEO)
Before I get into why this SEO tutorial is the perfect starting point for your learning journey, let me first give you some context on why I decided to make this 5 video, 9000+ word guide.
When I first started learning SEO, I found the guides to be either be too high level, too detailed, or too fragmented.
As a beginner, I just wanted to understand the big picture first, and then start getting into the specifics.
That’s what this beginner’s guide is all about.
Whether you prefer watching video or reading text, I’ll take you through the core concepts of what it takes to be successful with SEO.
If you want to know how to get your SEO content ranked highly in Google fast, this guide is the place to start.
After reading this article, you will have a clear understanding of exactly what SEO is, how Google ranks websites, and, most importantly, how you can play the game the right way so that your content ranks on the first page of Google for years to come.
This is an incredibly in depth guide so you might want to bookmark this page and refer back to it as needed.
These concepts take time and patience to master so sit back, relax, and get ready to take some notes.
We are about to level up your search engine game… Forever.
Before we get started, it’s important that we have a clear understanding of what search engine optimization actually is.
According to Search Engine Land, SEO:
…stands for “search engine optimization.” It is the process of getting traffic from the “free,” “organic,” “editorial” or “natural” search results on search engines
In layman’s terms, SEO is the art and science of optimizing your website and content so that it organically appears on the first page of Google (or any other search engine) for your respective high-intent keywords or phrases.
For example, if you run a local marketing agency in Denver, having your website optimized for Google would mean that when someone types in “Best marketing agency in Denver” your website would be on the first page.
The Importance of SEO
One of the first questions that inevitably pops up for many business owners and online marketers is “Do I really need to practice SEO to achieve long term success?”In a word? YES!
If you will recall our previous definition of SEO, “It is the process of getting traffic from the “Free”, “Editorial”, or “Natural” search results on search engines”.
This is an important distinction to make because, unlike product marketing or other traditional marketing methods and paid traffic, SEO is the process of earning free visitors on autopilot for years to come.
If you optimize your website properly according to SEO KPIs, you will experience a massive influx of organic visitors (read: potential customers) without spending a single dime on advertising or marketing.
What would that do for your business?
How would your life change if each and every day you had thousands of highly qualified leads being attracted to your website… automatically?
I don’t think I need to spell things out any further.
SEO is, without a doubt, one of the single most important marketing strategies of today and, if you can get this right, you will never have to worry about your bottom line ever again.
Do I have your attention now?
I hope so!
What Google Wants
What does Google want?
At the end of the day, it’s important to remember that Google is a business like any other.
However, unlike most businesses, their product isn’t a piece of information or a physical object, it’s access to relevant content.
As a business, Google’s goal is quite simple.
They want to figure out what their customers are searching for and then provide them with the most relevant web pages possible.
It’s that simple.
Think of Google as the world’s most effective librarian.
There are millions of “books” or search results in the online library (aka the internet) and it’s Google’s job to help you find the most relevant “books” for your specific questions and concerns.
If you search “How to gain muscle” or “How to find love” or “How to do SEO”, it’s Google’s job to provide you with the most relevant and valuable content related to your query.
Fortunately or unfortunately, there is no way to change what Google wants in order to make our existing content and web pages more appealing.
Instead, our job is to play nice and give Google exactly what it wants.
And the only thing that Google wants is highly valuable content.
It wants content that is:
- Trustworthy, credible, and authoritative
- Unique
- Popular
- Useful and informative
- Neither deceptive nor malicious
- Highly valuable!
But the question still remains, “How in the world does Google actually know what content meets these criteria?”
How Google Finds the Most Valuable Content
While human beings have five senses, Google has only three “senses” for finding and determining the value of content on the internet.
- Google Bot
- Traffic Data
- User Metrics
Each of these “Senses” or methods for finding and ranking content is important to understand because it will have a tremendous impact on our ability effectively optimize our content.
Here’s an overview of how they work.
Google Sense #1: Google Bot
The first of Google’s three “Senses” is the Google Bot.
Googlebot “crawls” the internet in search of new and updated web pages and links.
Once it finds the information that it’s looking for, it will then take that information back to Google’s data center where it is stored and organized in a supermassive database known as the Search Index.
If Google were a treasure hunter, you could imagine Googlebot as their proverbial metal detector.
It scans the earth (internet) in search of treasure (high value websites), but it will pick up anything that is made of a metallic substance (e.g. any website).
Much like a metal detector, Googlebot isn’t responsible for sorting or deciphering what it finds. It’s sole purpose is to find and index content so that other programs, such as Google’s RankBrain (which we will discuss later) can rank it.
The four ways that Googlebot searches for information are:
- URLs
- Metadata
- Anchor Text
- Content
Here’s a quick overview of how you can optimize each of these factors to be more easily understood by Googlebot.
Your URL: From Google Bot’s Perspective
A URL or, Unique Resource Locator, is the method that we use to find a single specific web page.For any given URL, there can only be one web page, and this is an integral part of how the internet works.For example, if you type in https://www.linkio.com you will always land at the Linkio home page, you will never be taken to a different site or a different page unless the web page owner sets up a 301 redirect (but that’s a topic for a different time).
In order to optimize your URLs, you must first understand the three types of URLs that are present on the internet.
1. Home page URL: https://www.linkio.com
2. Inner page URL: https://www.linkio.com/seo-tutorial/
3. Sub-domain URL: https://app.linkio.com/
A common SEO practice that still works today but worked better a few years ago was purchasing an Exact Match Domain or EMD to get an SEO edge.
Basically, you purchase a domain name that contains the exact keyword that you want to rank for.
For example, If i wanted to build a business around SEO tutorials, I would have bought the seotutorial[dot]com domain name.
In 2010, I’d have ranked for SEO tutorial quickly.
But ever since 2012 when Google announced their EMD filter, websites that appear to be scamming Google by exactly matching their URL to their desired search query are having their website lowered in the SERPs.
And it’s no secret a lot of SEOs had their businesses brought to zero by this update.
In fact, around this time, I owned about 200 plumbing websites for just about every city in Orange County.
It was the same type of pattern for each one, i.e. emergencyplumberirvineca[dot]com.
Every time the phone rang, my plumbing client would write me a check.
But after this update, the sites were a lot more difficult to rank.
So what does this mean for you?
If you don’t have an existing domain name already, then you might consider purchasing a domain that has some keywords present but isn’t an EMD.
For example, if I wanted to really focus on SEO tutorials, my domain name might be tutorialsbyajay[dot]com or seobyajay[dot]com instead of seotutorial[dot]com.
Just think of it this way when choosing a domain name: what name can you pick that will give Google and your visitors a pretty good hint of what industry you’re in, without being overly blatant.
If you can’t think of a domain name that includes a part of your keyword, that’s also totally fine.
Just look at my domain name, Linkio. Even though we provide marketers with SEO tools, there is no mention of SEO or tool in the domain name.
Why?
Because there are plenty of other ways to optimize for SEO besides the domain name.
Next, let’s explore what else the Google bot is looking for as it crawls through the web.
Your Metadata: From Google Bot’s Perspective
Metadata, as the name implies, is information about other information.
For example, in the “Real World” we have social security numbers, VIN numbers, dates of birth, model numbers, and serial numbers.
On web pages, there are three primary types of metadata.
- Page Meta Title
- Page Meta Description
- Schema
These pieces of information are designed to help Google understand what your site is about so that it can rank it for the appropriate query.
Ironically, even though this information wasn’t originally intended for humans to interact with, they are actually the very first things that a person will see on the search engine results page (SERPs).
It’s important to note that the information you include (or don’t include) in your metadata can encourage or discourage people from clicking through to your website from the SERPs.
Optimized metadata is when the meta title, meta description, and schema are all technically accurate for SEO purposes.
For example, if you were a plumber in Newark, NJ, this is what optimized metadata would look like.
- Page meta title: Plumber in Newark, NJ.
- Page meta description: Licensed and bonded plumbing repair company based in Newark, New Jersey. Our prices can’t be beat!
- Page schema: Name Address and Phone Number (NAP)
- Local Business: This is the type of entity
- Name: Chris Plumbing
- Street: 22 Newark Avenue
- Town: Newark
- State: New Jersey
- Zip Code: 07101
If we go back, once again, to our library analogy, metadata is very similar to the cover of a book. In order to quickly and effectively find the information that you are looking for, the library needs to have an accurate book title (meta title), back cover (meta description), and identification number (Schema).
You could still find any book that you were looking for with only one of these three factors, however, having all three fully optimized makes it much easier to quickly find and obtain the information that you need.
Anchor Text: From Google Bot’s Perspective
Anchor text is clickable text in a hyperlink that’s on a webpage. Typically, you can recognize anchor text by the blue color and underline, although savvy web designers can customize colors to their liking.
Linkio, is an example of anchor text.
So is this.
As is this, The Ultimate Guide to Anchor Text.
When someone clicks on an anchor, the link is opened either on the same
page or in a new tab on your browser.
In the modern world of SEO, anchor text has become an even more important factor for effectively ranking your content than keywords.
I could write an entire guide focusing exclusively on anchor text, but for the purposes of this guide, I want to give you a brief runthrough of the different types of anchors and how you should use each to optimize your content for search engine success.
● Branded: This is an anchor that is associated with your brand name. For example, if you run grubhub[dot]com then your branded anchor text would be “Grub Hub”.
● Keyword: This is an anchor associated with keywords you’re trying to rank for. An example of a keyword anchor would be someone who is trying to rank for the query “Online Marketing Tricks” would be “Online Marketing Tricks” or “The best online marketing tricks”.
● Hybrid: A hybrid anchor is usually a combination of both branded and keyword anchors. For example, “Linkio’s beginner’s guide to SEO”
● URL: This is one of the simplest types of anchor texts. A url anchor is exactly what it sounds like, a URL. For example, https://www.linkio.com is a URL anchor and so is linkio.com
● Natural: Natural anchors are anchors that are not related to your keyword or brand. For example, click here, this website, and our new article are all natural anchors.
You can play around with our anchor text generator tool to come with more ideas for how to vary your anchors.
Content: From Google Bot’s Perspective
Content is anything and everything that can be viewed by your audience from the web. In your run of the mill article, there can be several types of content including:
● Written content
● Videos
● Images (such as infographics)
● Sound files
In order to ensure the highest ranking possible, it’s important that you clearly define what each piece of content is about by optimizing the metadata so that Google can quickly and accurately determine the topic of your content.
Content Type 1: Written Content
Written content is any text that appears on a web page. This spans everything from long form articles to single sentences to the headline above an image or video. If it can be seen on a website (by humans or Google) than it’s considered content.
Google will look for certain keywords and related phrases to determine what your content is about and how relevant it is to a given search query. This helps web pages rank in the SERPs.l
Content Type 2: Images or Photos
Any sort of photographic content such as pictures, infographics, charts, flyers, etc. are considered content.
This is something that many novice webmasters overlook but it plays a huge role in helping Google understand and effectively rank your content.
In order for Google to understand and view your content, you need to optimize the metadata for your specific keyword.
This includes the file name, alt text, and title.
Here’s an example of how you would optimize an image in WordPress for the keyword, “Guitar Lessons in Seattle”.
Content Type 3: Videos
Video files such as MP4s or MOVs are optimized for Google in the same way as image content with a file name, alt text, and title.
Content Type 4: Sound Files
Any sort of embedded sound files such as MP3’s are considered sound content. This must be optimized in the same way as image and video content to ensure that Google can properly understand and rank your content.
Pulling All The Content Types Together: The Importance of a Multimedia Experience
The online world is changing. In years past, it was normal for a website to focus exclusively on one type of content such as written blogs or video content (like YouTube).
Today, however, Google is placing an increased focus on webpages that offer a multimedia experience to their users.
In order to achieve the highest ranking possible, it’s important that you embed image, video, and sound files into your written content to give your users a more complete experience and Google a greater understanding of what your content is about.
Think about it this way…
If you were teaching a class of students about a particular skill, you are going to have different types of students who learn in different ways.
In the same way that there are kinesthetic, auditory, and visual learners, and your teaching style should incorporate resources and techniques that appeal to each one, Google wants web owners to provide a variety of content types both to increase its usability and the ease with which Google can understand it.
Google Sense #2: Traffic Data
Once a website has been crawled and indexed in Google’s database, the next step in the ranking process begins.
Since Google’s search engine has yet to achieve sentience, it has no direct way of determining the value or validity of any given website.
Instead, it looks for clues about the quality and value of a web page by paying attention to how audience members and other websites interact with that information.
The first way that it does this is by analyzing the amount of traffic that a given web page or piece of content receives.
Specifically, it looks for:
● Clicks on search results
● Chrome browser data
● Traffic data purchased from high traffic sites
● Traffic on sites that Google owns (such as YouTube)
● Adsense and Google Maps
It’s kind of like deciding which movie you are going to see based on how many other people are in line for a given film.
When Google is trying to determine whether or not a website has high value content, the first (although not necessarily the most reliable) way to determine the value of a site is by how many visitors it has.
However, with the abundance of paid traffic options available to your average webmaster, this isn’t always an accurate way to determine value.
In the same way that countless people can line up to see a terrible movie (I’m looking at you Transformers), a website with subpar content can still receive tons of traffic.
As such, Google has a third way of determining the value of a web page or piece of content…
Google Sense #3: User Metrics
Once Google has found and indexed a website and then analyzed the amount of traffic being directed to that site, it analyzes how users interact with that website in order to determine its value to searchers.
It does this by analyzing a variety of factors such as:
● The amount of time spent on a given URL (dwell time)
● The number of videos that are played and watched
● Advertisement clicks
● Clicks on internal and external links
● Button clicks (such as opt-in or purchase buttons)
Using the movie analogy I mentioned earlier, this would be like a staff member taking notes about how many people left a movie, fell asleep during the movie, laughed at specific jokes, or clapped during exceptionally pivotal scenes.
Google knows that it’s easy to buy traffic and game a “Quantity Only” algorithm so they place a special importance on user metrics when ranking and rewarding specific web pages.
For more ideas on how to generate great user signals that rank your page, check out this case study on how we ranked without backlinks.
What Happens Next?
Once Google has found and indexed a website, its traffic data, and user metrics, it will then analyze and rank those websites to determine which pages will show up first for a specific search query.
Google’s process for ranking content is known as the Google Algorithm.
Their algorithm is an incredibly complex series of mathematical equations that analyze data and then rank websites with the goal of presenting users with the most relevant possible content.
So, for example, if you searched “Beginner’s Guide to SEO”, Google wants to ensure that the first result they present to you is the best and most relevant piece of content on that subject.
Google’s algorithm uses a number of different factors to determine relevance and, over the course of this guide, I’ll be sharing the most important of these with you.
Differentiating White Hat and Black Hat Tactics
Before we go any further I want to leave you with a word of warning.
There are dozens of different tactics that you can use to improve your search engine rankings, however, many of them are designed to “Game” Google’s algorithm and gain an unfair advantage by using shady tactics.
This is known as black hat SEO.
Such tactics include:
● Creating duplicate content
● Keyword stuffing
● Invisible text
● Redirecting users to another website
● Buying backlinks from non-relevant websites
And I will be the first to say it.
These tactics work… for a while.
However, after more than a decade in the SEO game, I can confidently say that I’ve never seen a website sustain success with black hat SEO tactics.
Google’s algorithm is one of the most advanced algorithms in the world and the constant patches and updates are designed to ensure that anyone trying to game the system is penalized and punished for their sins.
Sure, you can leverage black hat techniques to achieve short term success. However, over the span of months and years, you will eventually incur Google’s wrath and have your website penalized or worse… De-indexed.
As tempting as it might be to try and shortcut your way to success, I must urge you to reconsider.
Although white hat SEO takes time, hard work, and patience, it pays off in the long run and can help you achieve financial and business success beyond what you previously thought possible.
I’ve published some month-by-month case studies to prove you can be aggressive with your SEO without crossing the line. Here’s my SEO case study of how I ranked this Linkio website and this is my e-commerce SEO case study on how I’ve ranked a side business.
Optimizing Your On Page SEO
Now that you understand what Google wants and how you can make it easy for Googlebot to understand your website, it’s time to discuss specific tactics for optimizing your website and content for performance.
Website Speed
By far one of the most underrated aspects of a successful SEO strategy is your website speed.
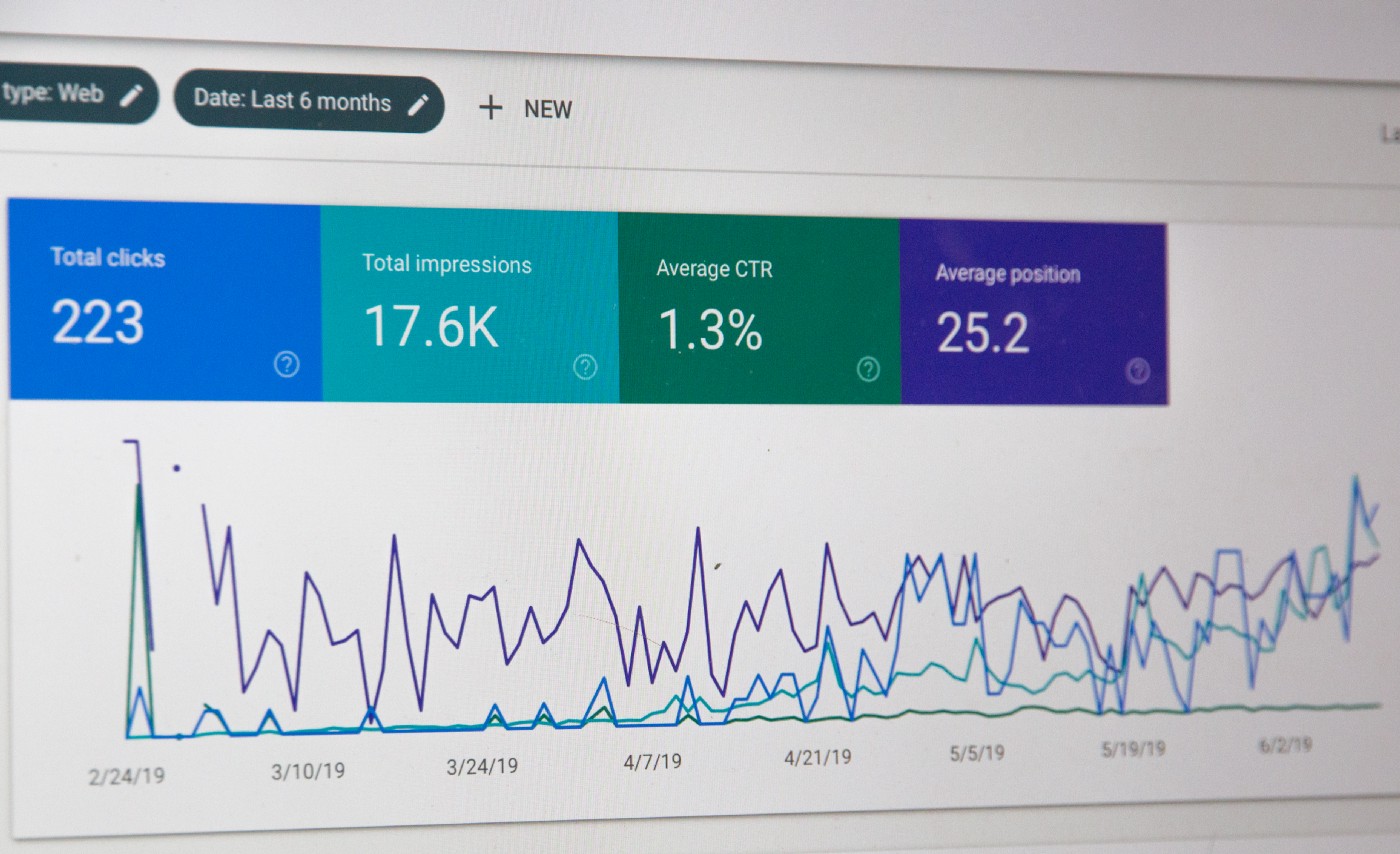
Google has estimated that websites with a 6 second load speed (or slower) lose more than 24% of their organic traffic due to sluggish page speeds.
But the reality is much worse.
47% of consumers expect a website to load in 2 seconds or less and more than 40% of them will abandon a website that takes longer than 3 seconds to load.
As such, improving the speed of your website is one of the most important things that you can do to improve user signals and traffic metrics and, by extension, your search engine performance.
But how do you actually get started boosting your website speed?
For a long time, I was guilty of disregarding site speed and just focusing on creating helpful content and tools.
Before I knew it, my WordPress backend had 90(!) plugins installed, 3 different page builders, and awful site speed scores.
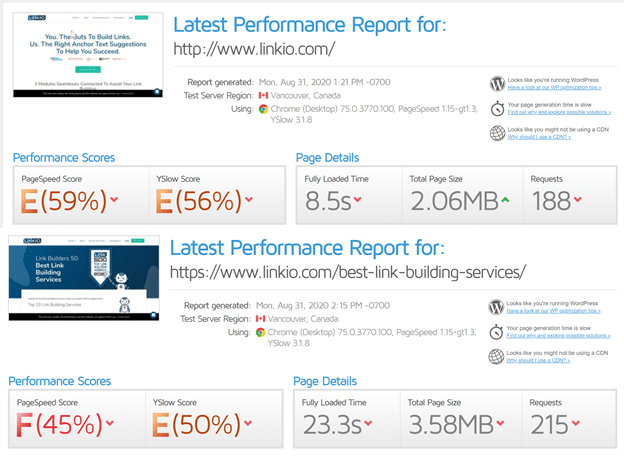
After making several changes, here are my current scores.
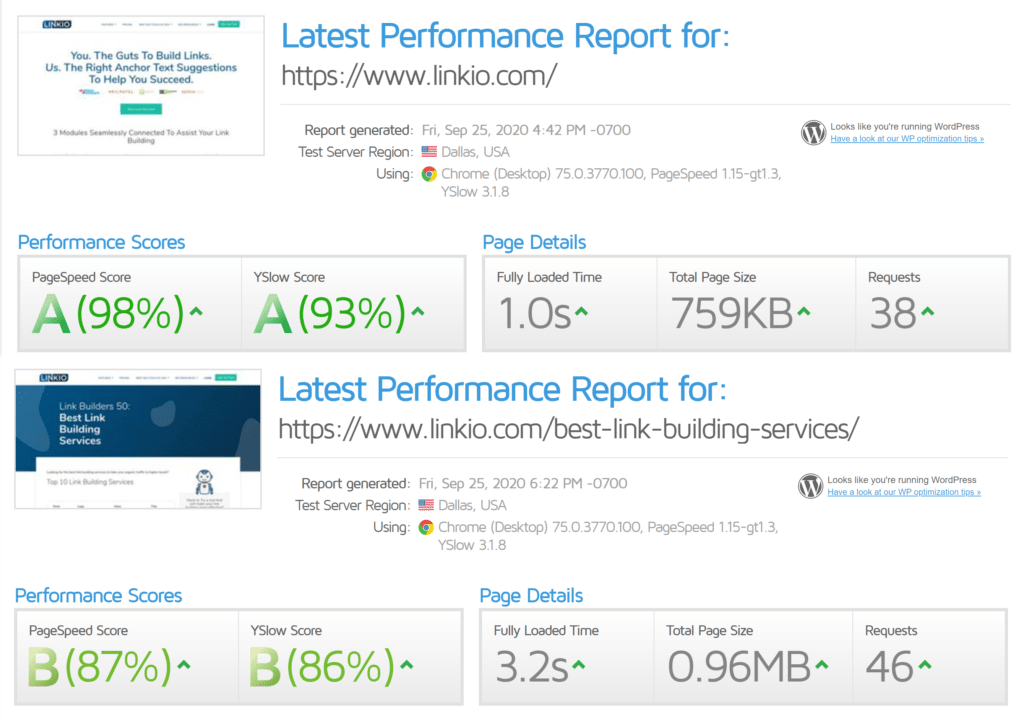
While there are dozens of great resources and tactics for ramping up your site’s speed, here are a few of the simplest and easiest things I did squeeze the extra speed out of my website.
Choose the Right Web Host
The first and most important thing that you can do to ensure that your website loads as quickly as possible is to select the right hosting package from the best company that you can afford.
There are four primary hosting options to choose from:
● Shared hosting
● VPS hosting
● Dedicated server
● Cloud Hosting
Shared hosting is by far the slowest and least effective type of hosting since you share resources such as RAM and CPU with other websites.
VPS hosting, on the other hand, is still shared with other websites but allows you to access a dedicated portion of the servers resources.
It’s kind of like living with a roommate vs. living in an apartment building.
When you have a roommate you share all of the resources such as living space, the bathrooms, and utilities.
When you live in an apartment, you are still living in the same building with other people, but you have your own dedicated area that is exclusively for you.
A dedicated server, on the other hand, is like living in your own house.
You don’t share any resources with anyone, however, the cost is greater and the technical requirements are much more taxing.
Finally, Cloud hosting is hosting your website through a cloud provider like AWS or Digital Ocean. No servers to manage and you typically pay for what you consume.
I switched from dedicated hosting to cloud hosting in haven’t looked back. It’s pretty technical to setup though, so it’s better to go through a managed-cloud provider like Cloudways, Kinsta or ManageWP.
The one I chose is Cloudways VULTR WordPress hosting. It’s pretty much one of the fastest options out there right now.
Minimize Image Sizes
Another common mistake that many newbie web owners make is that they forget to minimize the images on their website.
Oftentimes, stock photos will download at pixel sizes of 4500 x 4500 and up. Even if you proceed to resize the images in WordPress, your website will still have to load the full image and then resize it to the appropriate length and width, slowing your website even further. Therefore, make sure to use an optimized image to speed up your WordPress site.
I ended up using Imagify to bulk shrink my 4 gigs of media down to 400 mbs. You do notice the images get worst looking – especially since I chose the most aggressive settings, but I’d OK with it.
Enable Caching
One of the easiest ways to increase your website’s load time is to enable browser caching.
Whenever someone visits your site for the first time, their browser will have to load all of the elements on your site by sending an HTTP request to the server. This takes a lot of time and can result in very slow page speeds.
However, if you enable browser caching, their browser can load many of those same elements from its cache, or temporary storage.
This means that your repeat visitors will have a faster and cleaner experience which, of course, means a greater possibility of conversion.
I picked WP Rocket because most bloggers were recommending it. After installing it, it worked decently enough, but it honestly broke lots of things too. It’s default optimization options rarely work out of the box, unless your website is simple. I ended up hiring a developer and the first thing he said is how much he hates all caching plugins, including WP Rocket.
But I had noticed it’s lazy loading settings are quite useful, and I preferred a plugin over his custom solution because custom things are hard to maintain year after year.
So he begrudgingly help fix the stuff WP Rocket broke and the pages are loading quite well now.
If your website is simple, then simply install the plugin from WordPress then enable caching once it’s installed.
Audit and Enable Compression
When it comes to boosting your website speed, compression is the name of the game.
Start by running a compression audit at GID Network and then enable a browser caching software such as W3 Total Cache and select “Enable Compression”. I haven’t seen compression settings in WP Rocket though.
Limit Plugins and Other Third Party Software
Although I’ve already recommended a number of great plugins that you can use to speed up your website’s response time, it’s important to note that most plugins will hinder, not help, your website’s performance.
As such, it’s important that you minimize the number of plugins and third party software that you use.
If you don’t need ‘em, delete ‘em. Trust me, I know it’s easier said than done.
WordPress plugins are amazing and save a ton of time. But I’ve learned the hard way, there are tradeoffs.
While fixing Linkio’s speed, I’ve gone down from 90 plugins to 33.
Some will say 33 is still way too many, and they’re probably right. But I’m running a business and I need a robust awesome marketing site, so a little bloat is cool with me. I ended up using an awesome plugin called Asset Cleanup Pro that helps me selectively unload plugins sitewide with specific page exceptions.
You can test your site speed with GTMetrix and Google Page Speed Insights.
Website Design
Website design is a critical aspect of on page optimization. Although you won’t directly gain any points from Google for having an aesthetic design or beautiful visuals on your site, the importance of web design for user experience cannot be overstated.
If you’ll recall, one of the key factors that Google uses to determine a website’s value is dwell time or, the amount of time that individuals spend on a given page or URL.
And your website design will impact dwell time in a way that few other things can.
Sure, there are plenty of ugly websites that still rank highly in Google simply because of the celebrity status of their owner or the massive marketing budget behind them.
However, they are ranking in spite of their design, not because of it.
Just think about your own experience. How many websites have you visited and promptly left for no other reason than the layout and design of the site?
If you’re anything like me, the answer is “Hundreds!”
Don’t be like those sites.
If you haven’t done so already, I highly recommend that you invest in a responsive website design (there are plenty of themes that are surprisingly affordable).
It’s important that your website is optimized for mobile devices since Google is looking to roll out something known as their “Mobile First Index” later this year.
The mobile first index is exactly what it sounds like. After its launch, Google will begin crawling and ranking your mobile site first. This means that any website that is not fully responsive and optimized for mobile users will be penalized and experience a massive drop in its rankings.
I don’t care if you have to hire a web design company or redesign your entire site yourself. If you want to succeed at the SEO game in 2018 and beyond, you need to optimize your site for mobile users. Period.
Content
It’s been said that “Content is king”, and you can rest assured that the king still reigns supreme.
Without high quality content, none of the tactics or techniques that I’ve shared with you thus far will make a difference.
You can optimize your website all you want. You can have a killer backlinking strategy (which I’ll talk about in the next section). You can do everything right.
But without exceptional content that clearly shows Google that you are the authority when it comes to your target keywords and phrases… None of it will matter.
But what makes content “Good”?
Simply put… Context.
Here’s what I mean.
In the olden days of SEO, Google ranked web pages based on their content. In other words, the only thing that Google wanted to see was content that was stuffed with the target keyword.
Since then, Google’s algorithm has evolved and become much smarter.
Although it still cares about content, it places even greater importance on the context of that content.
In other words, Google wants to see content that covers all aspects of its topic, not just its respective keyword.
For example, if you wrote a piece of content teaching people how to gain muscle, Google would want to see you including dozens of long tail keywords throughout your article that are related to your specific topic such as:
● The best supplements for gaining muscle
● How to recover from a workout
● Gain muscle for beginners
● High intensity interval training
The key to creating comprehensive content that proves to Google that you are the authority on your chosen topic is simple…
Create highly valuable content that is difficult to replicate.
Yes, it’s hard work. You will need to pour several hours into any article that you create (just like I poured several days into this guide).
But at the end of the day, you can’t game the system. All of your content should be 2,000 words or longer and cover your given topic as thoroughly as you’re able.
Here are a few other tips to help you level up your content and improve your website’s search engine performance.
Use Clever and Benefit Driven Subheadings
Few people have the time or attention span to read through an entire article or mega guide these day. Just think about it…
Have you actually read all of the content up to this point? If so, then I salute you.
However, if you are anything like me (or 99% of the population) then you’ve probably been skimming through this guide, zeroing in on important headlines, and reading the parts that seemed important to you.
This is how most content on the internet is consumed.
In order to make your content as accessible as possible to your audience and thereby increase the dwell time on your important pages, be sure to break up your content with lots of subheadings, bullet points, and numbered lists.
The more skimmable your content is, the better.
Embed Lots of Images and Videos
They say that content is king, but it would be far more accurate to say that “Visual content is king”.
In recent years, we’ve witnessed an explosive growth in video and image based content like infographics.
The more videos and images that you can embed into your pillar content, the better the user experience will be and the more highly Google will rank your content.
It’s that simple. You can do all of this using common sense and a little bit of research but if you have more money than time, try using a tool like SurferSEO or free alternatives like Originality.AI. It’s basically a search scraper that tells you what words to include in your articles.
Don’t forget to link out generously to your relevant blog content or services pages throughout.
Understanding RankBrain and User Signals
The final piece of the on page SEO puzzle is something known as Google RankBrain.
According to Google, RankBrain is the third most important ranking factor that Google uses to determine how to rank a web page.
At the most basic level, RankBrain is a machine learning system that helps Google understand their search results.
While this might sound futuristic and incredibly complicated, it really isn’t.
RankBrain simply measures how users interact with the current search results and then changes the ranking accordingly.
Here’s how it works.
Let’s say that you search “How to invest in real estate”.
After looking at the SERPs, you decide to click on the #3 result. Upon entering, it’s the most comprehensive and in depth guide to real estate investing that you’ve ever read.
You spend nearly 40 minutes delving through all of the content and then bookmark the page to view later.
RankBrain is going to take notice of this and, if enough people have a similar experience, they will likely boost that result to the #2 spot.
Conversely, if you automatically click on result #1, realize that it’s a garbage article, and immediately exit, RankBrain will take notice and demote that result.
As you can see, RankBrain pays attention to only two factors:
1. The click through rate or CTR
2. The dwell time or time on page
I’ve already shared how you can increase your average time on page by creating more comprehensive content that is embedded with stunning visuals and videos (if you’d like to jump into that yourself, you’ll need an online video editor as a starting point), and now I want to take a minute to talk about optimizing your content for clicks.
The trick to optimizing your click through rate is simple.
Write a compelling and “Magnetic” meta description that people cannot help but click.
Let’s look at a couple of examples so that you can see what I mean.
Using the real estate investing query from before, take a look at the #8 search results meta description.

Notice how the description is clunky. It doesn’t make any promises or scream “Click Me!” the way it should. In fact, it doesn’t look like they optimized the meta description at all…
Now compare this to the #2 search result

Notice how the meta description is succinct, to the point, and makes a powerful promise.
When I read this description, my first inclination is to click on the article so that I can uncover the “Right” way to become wealthy through real estate.
This is how all of your meta descriptions should sound.
If you make a conscious effort to create compelling copy that entices readers and convinces them to click through to your content, the battle is yours and your content will continue to ascent the ranks (assuming that your content is valuable and comprehensive).
How to do Off Page SEO
With more than 2,000,000 new blog posts being published every day and more than 644 million websites currently being indexed by Google, it’s hard to grab the attention of humans and search engines alike.
Responsive design, and diverse anchor text you can still go completely unnoticed and be lost in the online crowd.
Understanding the Popularity Contest
In order to maximize your website’s popularity, you must first understand how popularity is determined.
When it comes to SEO, being ‘popular’ isn’t enough.
Just like there are cliques in high school, there are different groups within the realm of SEO. It’s our goal to be a part of the group that Google prefers.
| High School | Claim to Fame | Benefits | Risks | End Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hackers | Love to mess with the algorithm They get SEO results. | Rank first, rank cheaply, rank with less effort | Use hacks instead of best practices, ticking timebomb tactics | They’ll rank but eventually get penalized and have to start all over again |
| Greeks | Create amazing content, Really know their stuff | Create some of the best content of the web | Focus on the content, but not the promotion | Google likes the content but doesn’t think they are popular enough to show as number 1 |
| Emo Kids | Highly experimental Get discouraged easily | Willing to take risks and jumps into the SEO game | Vulnerable to getting impatient and quitting before the work pays off | They do things right and were on their way to getting results, but got discouraged and quit before Google acknowledged them |
| Jocks / Cheerleaders | Highly popular Not as focused on academics | They generate the right popularity signals for Google | The content they create may not be up to Google’s standard | They might rank well on the sheer power of their popularity, but eventually, Google could de-rank them because of poor user engagement signals |
| Hipsters | Like to experiment with new things. | Always looking for the latest SEO edge | May think the basic are played out and chase new stuff | They optimize for new things like voice search and latest best practices but ignore foundational activities of building popularity |
| Preps | Academically inclined and popular too | They can create great content and they can be popular | Might play it too safe, not aggressive enough | This well-balanced approach to SEO would have the best chance to succeed |
While it might seem boring to be in the “Play it safe” group, you can rest assured that, in the long run, this is the strategy that Google prefers and rewards.
So how do you increase your website’s popularity the right way?
Simple… By earning highly authoritative and relevant backlinks.
Domain Authority
The first, and arguably most important, aspect of a backlink quality is the domain authority of the linking website.
The best way to think this is in terms of referrals.
In the real world, different referrals hold different levels of importance with potential employers and clients. Companies also prefer to launch a customer referral program which allows more room for building trust towards their brand.
For example, a referral from your mother probably won’t hold much weight when it comes to getting that sweet new tech job. However, a referral from a C-level executive at a famous Fortune 500 company will have clients and employers knocking down your door to work with you. So, whether they use an employee time tracking or special task management tools, you will be ready for it all.
Backlinks are the same way.
Earning or purchasing a backlink from a low domain authority website (anything under 30) isn’t going to do much in terms of boosting your search engine success.
However, earning a backlink from a high quality website with a high domain authority can give you an (almost) instantaneous ranking boost and loads of SEO ‘Juice’ for years to come.
But this is just part of the picture. After some of the more recent updates to their algorithm, Google has begun placing a higher premium on the relevance of the linking site as well.
Backlink Relevance
Google doesn’t just want to see people earning authoritative backlinks. In order to rank a site highly in the SERPs, Google also wants to see a high degree of relevance in your backlink profile.
What does this mean?
Think about it this way.
Imagine that, once again, you are approaching a new client who has requested referrals for a marketing job.
As you flip through your Rolodex you have two primary referrals that you are debating between sending them.
The first referral comes from a high ranking executive in a well known company, however, the referral is related to a commission only sales position that you held more than five years ago.
The second referral comes from a relatively unknown entrepreneur who you’ve been consulting over the past six months. You’ve helped the client in question more than double the efficacy of their marketing campaigns and drive their revenue through the roof.
Although the first referral is undoubtedly more authoritative, the second is far more relevant to your desired position and, if you were forced to choose between the two, it would be a wise move to send your new prospect the second referral.
SEO works the same way.
Google wants to see sites that not only have high DA backlinks but backlinks that are highly relevant to their particular niche.
For example, if you want to rank for the term “Link Building Software” then you could get a link from a general online marketing site and it would still be a ‘good’ link.
However, getting a link from a slightly less authoritative site with the keyword “Link Building” in the title or URL would be a better and more relevant link.
As you develop your link building strategy and campaign, it’s important to keep this fact in mind.
The more closely related to your niche a given website is, the more importance Google will give that backlink.
Although I don’t have the space to dive into specific link building strategies, you can check out my blogger outreach guide for step-by-step ideas.
We've also compiled a list of the best link building agencies to help out in this area.
Schema Helps Google Understand Your Site
The Schema Markup is a tricky concept to understand and even trickier to implement. However, if you’re willing to suffer through the learning curve, it can provide a much needed boost to your long term search engine success.
Schema is a type of metadata that you can add to a web page to provide more information about the content to Google so it can display more relevant and informative results to users.
For example a cinema may have schema markup such as:
● Movie times
● Movie titles
● Address
● Phone number
When properly executed, schema helps clear up any ambiguity that Google may experience when trying to determine what your content is about.
For example, searching the phrase “New Book” without schema would leave Google to wonder whether you meant
● A book that is new
● A business named “New Book
● A book named New
● A new edition of a book
When you implement schema into your toolkit of search engine tactics, you can clearly and precisely tell Google exactly what your web page is about.
Here’s an example to help you understand this concept a little better.
Imagine that Google crawls your website and saw the following data:
● New SEO Guide
● New SEO Guide is Here
● Company
● 704-444-4444
This doesn’t make much sense to Google because there is no clear definition of what this information means.
However, if we add schema or a title to each piece of information, Google can instantly determine the significance of the information.
● Page Title: New SEO Guide
● Page Description: New SEO Guide is Here
● Anchor Text: Company
● Phone Number: 704-444-4444
Think of schema like Google’s version of a filing cabinet.
Anytime that it crawls a website and finds new information without schema, that information is simply dumped into the index without any form of organization… This doesn’t do Google or your SEO much good.
However, when you include a schema markup, your information is clearly organized into neat “files” so that Google knows exactly where to store it within its database.
Does this make sense?
Now that you have an understanding of what schema is, let’s talk about how you can implement it on your website as quickly and painlessly as possible.
Getting Started with Schema
Go to Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper and Select Your Data Type and URL
The first step in getting started with schema is to go to Google’s Structured Data Markup helper.
From here, you are going to select the type of content that you wish to markup. For the sake of this example, we’re going to use “articles” since it’s the most common.
Then, with your content type selected, copy and paste the URL that you wish to markup.
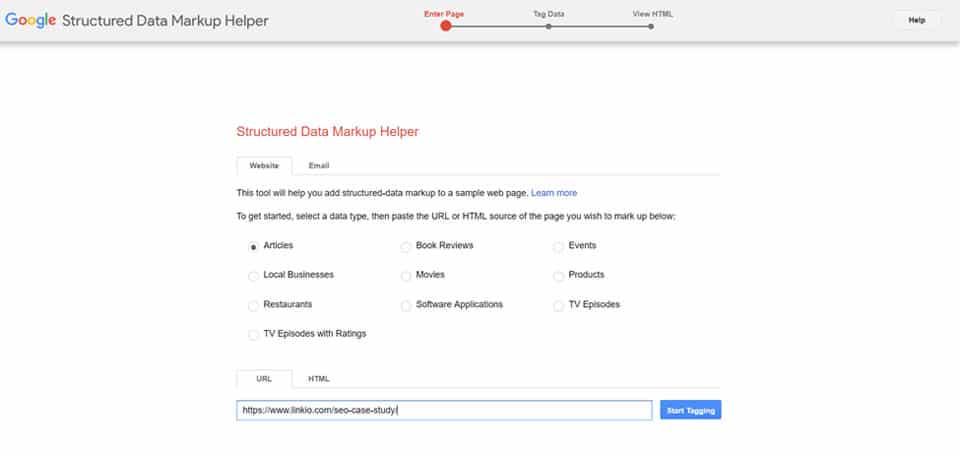
Click “Start Tagging” and then move on to the next step.
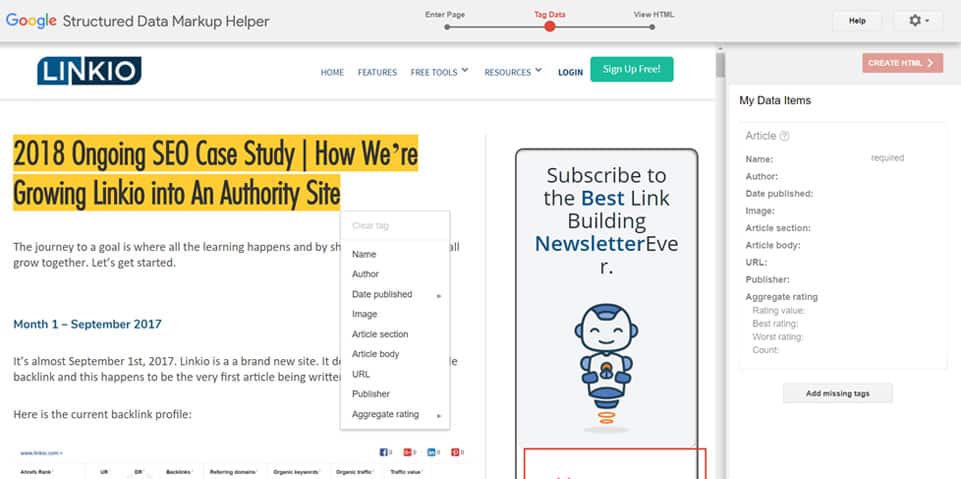
Select the Elements that You Wish to Markup
Once you are inside the markup helper, you can begin highlighting and tagging different elements on the page from the title, author, date published, images, etc.
It’s ok if you can’t effectively tag everything (you probably won’t). Just do the best that you can and try to get the biggest elements taken care of.
Create the HTML Code and Add it to Your Website
Once you’ve finished tagging all relevant elements, you are going to click “Create HTML” in the upper right hand corner.
From here, you will be given a HTML code that you can then download and import into WordPress or whatever other content management system you are using to power your website.
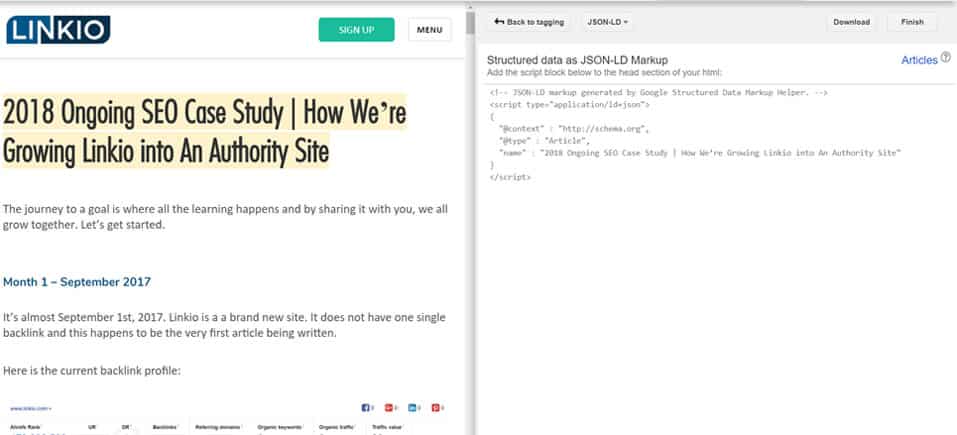
Simply copy and paste the highlighted snippets into the appropriate spots in your HTML code and Voila! You’ve successfully implemented schema on your website.
I recommend that you head over to schema.org, a resource created by multiple search engines, in order to gain a better understanding of how schema works and how you can effectively implement it into your search engine optimization efforts.
Although schema is relatively easy to implement, most businesses have yet to take advantage of this powerful tactic and, by getting started now, you will have a competitive advantage over your competition that can mean the difference between a first page ranking and getting lost in the internet forever.
SEO Quick Tips
Now that you understand your core SEO strategy, I want to leave you with a few quick tips for additional search engine optimization in 2021 and beyond.
Place an Importance on Voice Search
Voice search is growing at a rapid pace. Considering that more than 40% of adults perform at least one voice search per day, it’s important that you make a conscious effort to rank your content for voice searches. So how do you actually rank for voice searches? Well, the first step is to get your content on the first page. Once you’ve accomplished this goal by following the strategy I’ve outlined in this guide the best way to rank for voice search is by creating question and answer based content. For example, if you wanted to rank for the voice search “What is SEO”, you would want to create a piece of content that asks and answers that question like this: So what is SEO? SEO or search engine optimization is the act of creating and optimizing content that will appear “Organically” in a search query and drive free traffic to your website.
Encourage Comments and Social Shares
I think commenting is dying fast as more people hang out in Facebook groups, Slack channels etc, but if you have an engaged audience that likes interacting with your blog, GREAT! because Google will love all of that engagement.
Get Active on Social Media
Although social media doesn’t have a direct impact on your search engine performance, it is a powerful tool that can drive traffic and engagement and help your content achieve virality. I suggest that you pick 2-3 social platforms (I prefer Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn) and go all in on your profile. Share your content regularly, build a user base of raving fans, and encourage people to share and comment on your posts. Use special tools to post to Instagram from Mac so that you have the best content quality possible. The higher your engagement rate on social media is, the more traffic you can drive to your website, and the higher you will rank in the search engines.
Become an Influencer Maniac
One of the fastest ways to improve your ranking is to develop relationships with high level influencers who can help you generate high quality backlinks through reciprocal link building and guest posting. Engage with top influencer content. Regularly share their posts and articles. Link back to their content from your own website and try to find any way that you can to build rapport and gain their trust. The more influential web owners you have in your corner, the easier it will be to dominate the search engine game in 2018.
Leverage Quora to Indirectly Rank Your Content
If you are not doing so already, I highly recommend that you get started on the question and answer platform, Quora. Quora is quickly becoming one of the largest social sites on the planet and it’s based entirely on influential individuals sharing their expertise with others. If you regularly create high quality content on Quora and answer the right questions, you can have your answers ranked on the first page of Google for specific key phrases. Quora is also an excellent way to generate high quality backlinks as editors from Forbes, Inc.com, The Huffington Post, Entrepreneur, and Times regularly do content syndication of answers from Quora and publish them (and the links to your content) on their websites.
Produce Helpful Content
Google has its crosshairs on AI content and SEO content. The content is so humanly generated thanks to the text data gathered from annotated texts of real human writings. Writing for the user first and then optimizing for SEO afterwards will keep you safe with Google while making your customers love you. That's a win-win.
Conclusion
I hope that this guide was able to simplify SEO and help you understand the core strategies and tactics required to get your content to the top of Google’s SERPs.
Now it’s your turn.
Use what I’ve shared with you to accelerate your search engine success, drive thousands of new visitors to your website, and experience an explosive growth in your company’s bottom line.
I’ll see you at the top!
